|
|
 |
 |
|
Ihr Partner für leistungsfähige Bindemittel und Additive
|
|
|
 |
|
|
 |
 |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
|
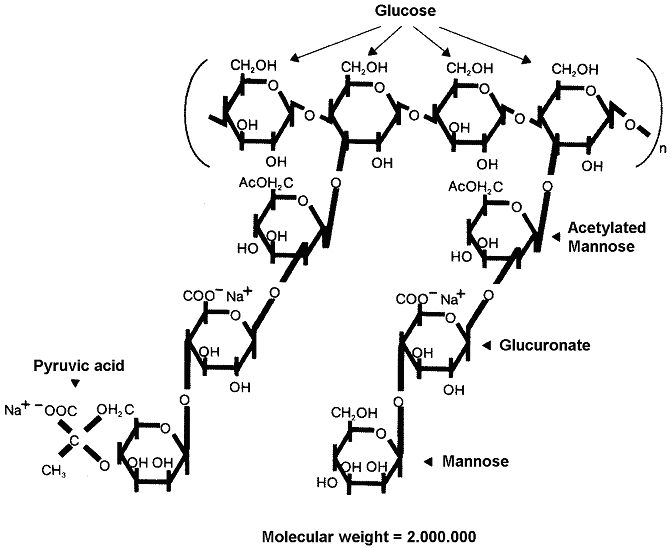
What is Xanthan Gum?
- It is produced by fermentation and extraction from the bacterium Xanthomonas campestris.
- The backbone chain of the polymer consists of ß-D-glucose-units which are associated in 1,4-position with each other.
- In position 3 of every second glucose-monomer-unit a trisaccharide side chain is linked.
- The XANTHAN-molecules are anionic by carboxyl groups at the side chains.
- The described chain exists as a single, double or triple helix.
- The molar mass of XANTHAN is approx. 2 · 106 with narrow distribution in comparison with most polysaccharides.
- A complex net of rodlike coils is formed by intermolecular associations.
- Therefore XANTHAN-solutions show pseudoplasticity.
- This highly ordered net is responsible for the high yield point of XANTHAN which results in a very good suspensibility.
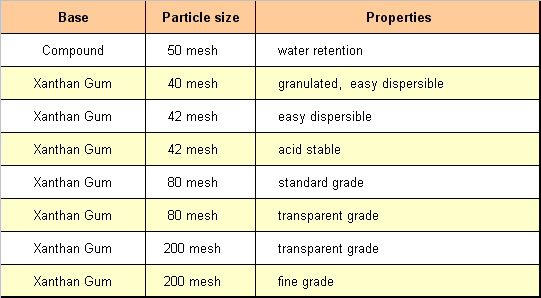
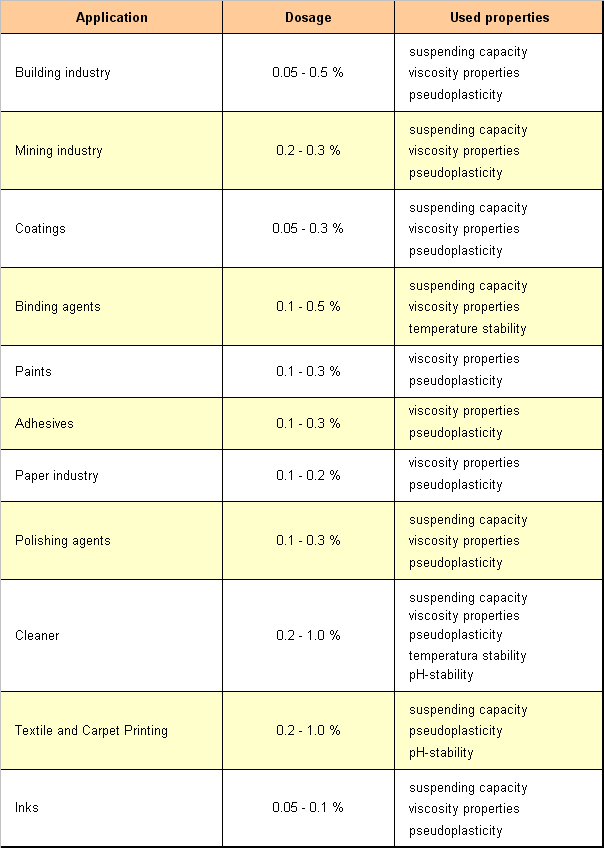
Main properties
- Low dosage, usually between 0.05 and 0.3%.
- Stable against lasting shear forces and high temperatures.
- High viscosity in case of low shear forces, decreasing viscosity in case of increasing shear rate.
- Stable in acid and alkaline systems.
- Compatible and stable in high concentrated salt solutions.
- Prevent the separation of suspensions from solid substances or oil drops.
- Stabilize emulsions and foams.
- Compatible with high concentrations of water-miscible and non-ionogenic tensides.
- Good solubility in hot and cold water.
- Forms easy pumpable and pourable solutions.
|
 |
|
|
 |
|